It is nothing but a system used to manage the various content(data,images,videos,etc..) used for various purposes.
What are Content Management systems?
CMS is a collection of procedures used to manage work flow in a collaborative environment.
Definition:
A computer software system for organizing and facilitating collaborative creation of documents and other content, especially for loading to a website.
What is Web CMS?
The processes and procedures used in the creation and management of web content is called web CMS.
With Web CMS the user can,
- Design
- Perform Content Updates
- Work with Dynamic Content
What can CMS do?
Allows web page updates using an ordinary web browser (e.g. IE, Firefox, Safari, Mozilla etc.). Reduces overall work as those responsible for content can update it directly and submit it for approval.
Allows different access levels for individuals with different roles (e.g. Marketing, Managers, etc). Enables documents to be published for fixed terms; older versions of documents can be re- used (versioning).
The Sites that tracking code built-in.
Easy to manage simple content pages.
Basic Features of CMS:-
- Access Control: Who is allowed to do what?
- Version Control: Return to a previously saved version.
- Library: Page templates, images, other assets.
- Content Repository: Text and other assets stored in a database or XML repository.
- Publishing Functionality: Creates web pages using content and templates.
Types of CMS:-
There are different types of CMS
Web CMS (WCMS)
Web CMS allows users to manipulate web pages without the requiring technical skills. This is applied to intranets, websites and extra nets.
Enterprise CMS (ECMS):-
These systems handle content and assets and also records other information such as the structure of the organization. This is a formal system and includes a wide range of processes and tools.
There are different types of CMS:
Mobile CMS (MCMS):-
The mobile industry is rapidly growing, hence there is a demand for content delivery on mobile devices. The MCMS were originally designed for business to customer (B2C) and also business to business (B2B).
Component CMS (CCMS):-
CCMS allows granularity, a paragraph of content is stored in the system and can be used by a document or a series of documents.
How does a CMS work?
Basic information flow in a CMS includes?
1. Template designed
2. Content is entered as plain-text or HTML into database
3. Content is placed in a template for display to the end user

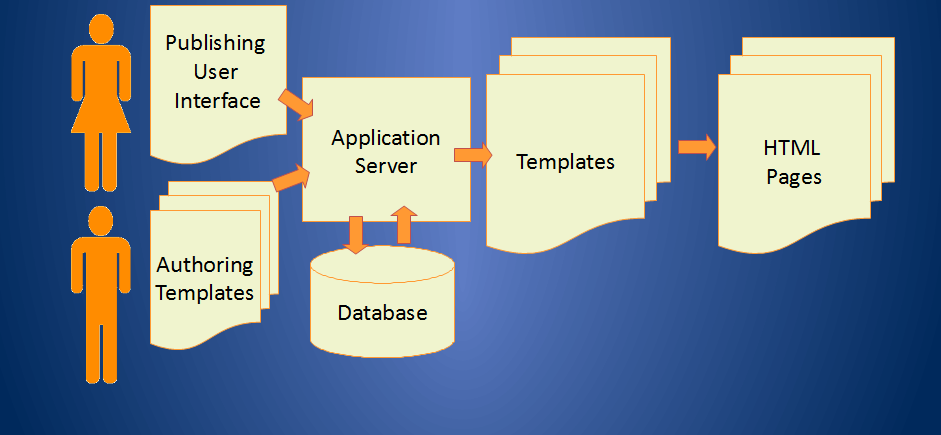
The components of CMS:-
The CMS is made up of the following major systems:
- Application Server Database.
- Authoring Templates.
- Publishing User Interface HTML Pages Templates.
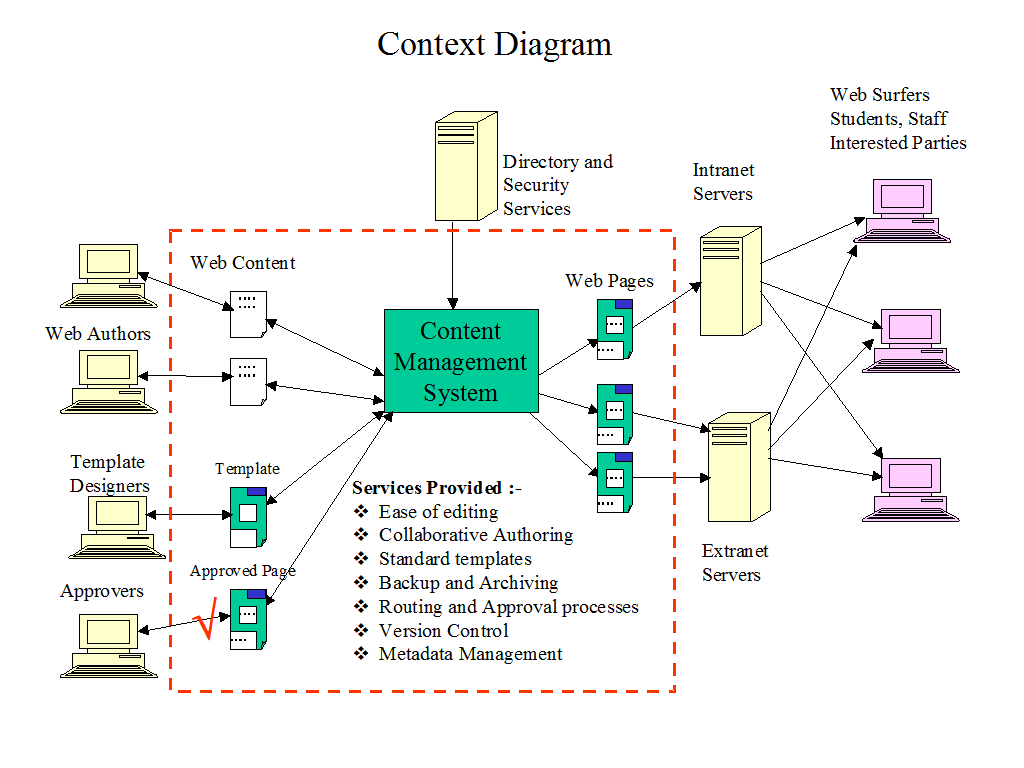
The Basic CMS Architecture Web Authors Context Diagram Content Management System Intranet Servers Extra net Servers Web Content Web Pages Web Surfers Students, Staff Interested Parties.
Services Provided:-
- Ease of editing
- Collaborative Authoring
- Standard templates
- Backup and Archiving
- Routing and Approval processes
- Version Control
Metadata Management Directory and Security Services Template Designers Approvers.
The Metadata Work flow Process Author Creates Content CMS applies Metadata Approver checks Work Metadata sent to the Search Engine CMS publishes to the web servers Approved Not Approved Available on the web.
The basic architecture of CMS is shown below,
Benefits of using CMS :-
CMS are Web development platforms designed to simplify content creation and management.
CMS allows to Create, Manage, Measure, Optimize and Modify content.
Simplifies web site development and maintenance without the need for technical skills.
CMS reduces cost and time in developing and maintaining web sites.
CMS allows the integration of different web based technologies.
CMS can handle Web 2.0.Allows ‘Dynamic’ We page creation.
Allows visitors to create their own web page designs.
Provides may ready made templates for content porting and publishing quickly.
Visitors get engaged more due to the flexibility in web site.
Dynamic content keeps visitors engaged with the site.
Content automation is the major benefit and this simplifies many development tasks.
Improves the quality of the company web sites.
The implementation of standards across presentation, metadata, governance, and navigation will enhance quality.
Ease of use will remove some of the barriers to quality.
The dimensions of quality in this instance are accuracy, availability, discoverability, relevance, and timeliness of information.
Accuracy: Enables the approval process to confirm the accuracy of the information.
Availability: Ensure that the information is published, backed up, versioned, and restorable through automated process.
Discover ability: Ensure that the information can be located through effective use of metadata driven searches.
Relevance: Enable a process to ensure relevance through the use of approval processes. Timeliness of information: Simplify and automate the publication of web site information and enable removal of information through the use of automated scheduling processes.
Efficiency: Allows direct content creation.Page appearance controlled from a collection of central templates.Navigation aids and links are generated automatically.
Centralized Updating:
- Links can be quickly added for all sites.
- Text can be changed for all sites it appear uniform.
- Navigation features are simplified for all sites.
- All management is done from a central interface or template.
Emerging Management tools:
- Mobile content.
- Digital Video content, Flash driven content, etc.
Content Scheduling and Content Integration:-
- Content can be set to a timer.
- Content can be displayed only during a specified period.
- Content can be erased/hidden after a specified period.
- Many CMS comes with own blogging software.
- CMS can inter-operate with other popular blogging software.
The Inevitable Changes
Web development team could be reduced or vanished .Some parts of the site can be updated directly by staff . Look and feel would have to be more consistent. More staff time is focused on special projects rather than day-to-day updating.
Preparing for CMS:-
Requires many skills: writing, gathering assets, designing a temple driven website and authoring templates, technology implementation, workflow… . Requires coordination across diverse departments and roles. Requires rigorous project management .
The CMS design and technology is tightly integrated. CMS configuration is technical work and often performed by information technologists .Yet many tasks for example, creating authoring templates, require a well-designed user interface for content authors.Therefore, designers must be proactive and find/learn where their skills are needed.
Content is not neglected .The focus is much on design and implementation.More attention is needed for content creation and migration.Ultimately, the CMS is implemented to deliver content – hence it has to be prioritized appropriately .Migrating old content into CMS will always take longer than expected.Reusable content requires standardization.
Standardization is done on many levels:
- Format of Information.
- Web Sites/Intranets
- Metadata
- Authoring and Publishing Templates
- Require collaboration and coordination across an organization
The CMS Framework are:-
- Establish metrics
- Size of company
- Project management proficiency
- Degree of centralized content management processes
- Type of content
- Variety of content
- Variety of publishing channels
- The content to be managed
CMS Options-Explored Implementing a CMS is more for… Comfort-finding the right tool Support Safety and simplicity in web content and web site/intranet maintenance. Most CMS have popular development tools Most CMS have support communities ,CMS offers specific tools for specific designs and features.
CMS Options-Explored :-
There are two major categories of CMS:
- Proprietary CMS
- Open Source CMS
Proprietary CMS:
In this system some other company owns license to the CMS application and the client company can use their CMS for maintaining its web site .
Proprietary CMS has many limitations. Services on the web such as ‘Build it yourself’ websites run on proprietary CMS.
Open Source CMS :-
Open Source CMS are cheaper with no licensing fees, easier to use and no contracts required for long term use, Popular open source CMS runs on PHP.
Some commonly available tools are Word Press, Joomla, Drupal, etc. Free modules, plug-ins, and tools are available along with thousands of templates.
CMS tools are designed to offer a wide range of solutions and applications ,Open-source CMS tools provide plenty of room for development and evolves through community cooperation .Open source CMS allows developers from across the world to participate in creating something new
Buy a CMS to suit the company’s needs Content: CMS: Digital Asset Management Source Code Management Document Management Web Content Management MultimediaSoftware CodeDocumentsWebsite content
Heterogeneous content requires more tough standardization decisions Easier to standardize Harder to standardize Low level of variation among content items, pages, site sections, and sites High level of variation among content items, pages, site sections, and sites.
The steps to make CMS ready are:
- Install the CMS
- Configure the required specifications
- Apply the visual design
CMS: Up and Running • Content is the winner – visitors are more frequent and they have a reason to come back • Social media integration helps visitors to get involved and share with others • Dynamic web site creates an opportunity for frequent updates. Visitors are able to generate more content
CMS offers features to control the website:
- Email accounts
- Backup tools
- Analytics tools
- Software tools
- Create semantic relationships
Bigger sites (>100K pages) require more than efficiency, they require automation. Even with reusable content, it’s not cost- effective to touch every piece of content on every type of page ,Once content is authored, only touch each type of content Accomplished via a Semantic CMS…
Inventory all content present on current site . Port it all to some non-HTML format (word, text) ,Input into CMS Set up linking and site structure,Set up user accounts,User Training.
